Die grösste Apple-, Macintosh- und Powerbook-Sammlung
mac os classic
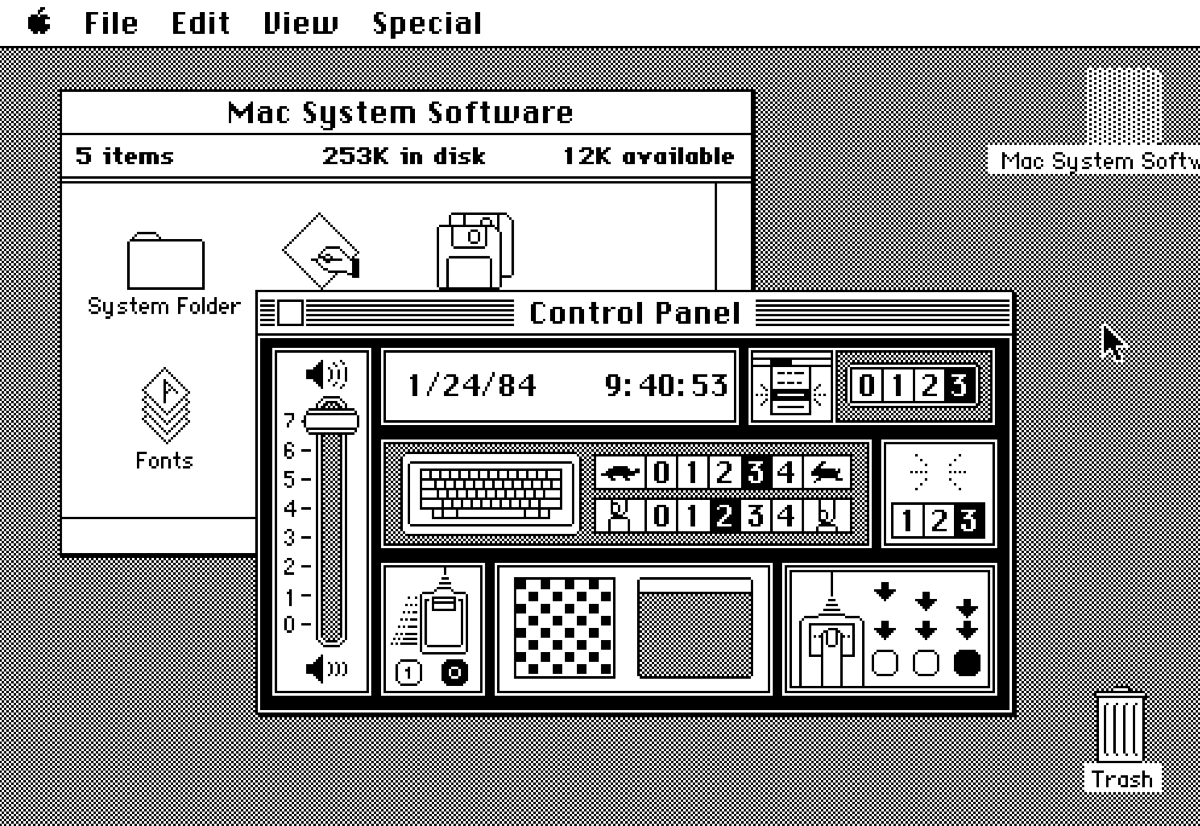
1.0
Januar 1984
68000 prozessor or later,
128 KB of RAM
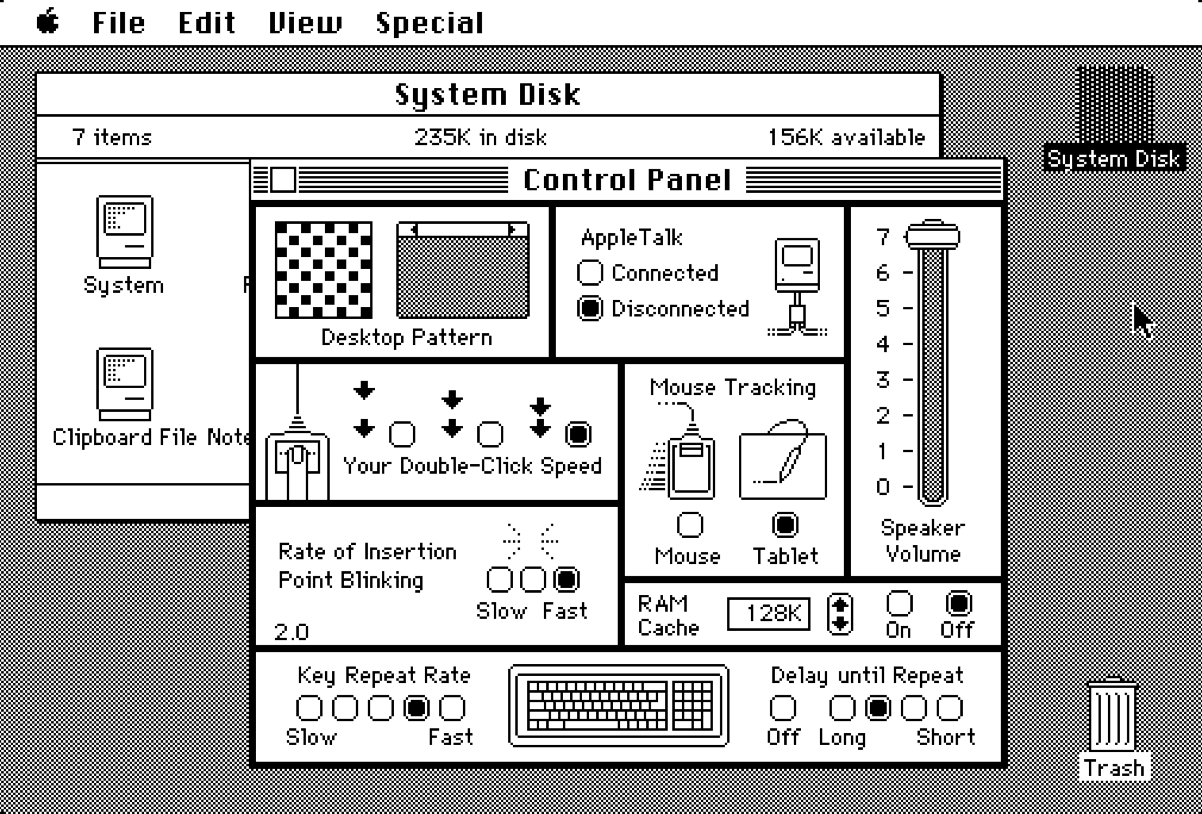
2.0
April 1985
68000 prozessor or later,
128 KB of RAM
3.0
Januar 1986
68000 prozessor or later,
128 KB of RAM
4.0
Januar 1987
68000 prozessor or later,
512 KB of RAM
5.0
October 1987
68000 prozessor or later,
1 MB of RAM
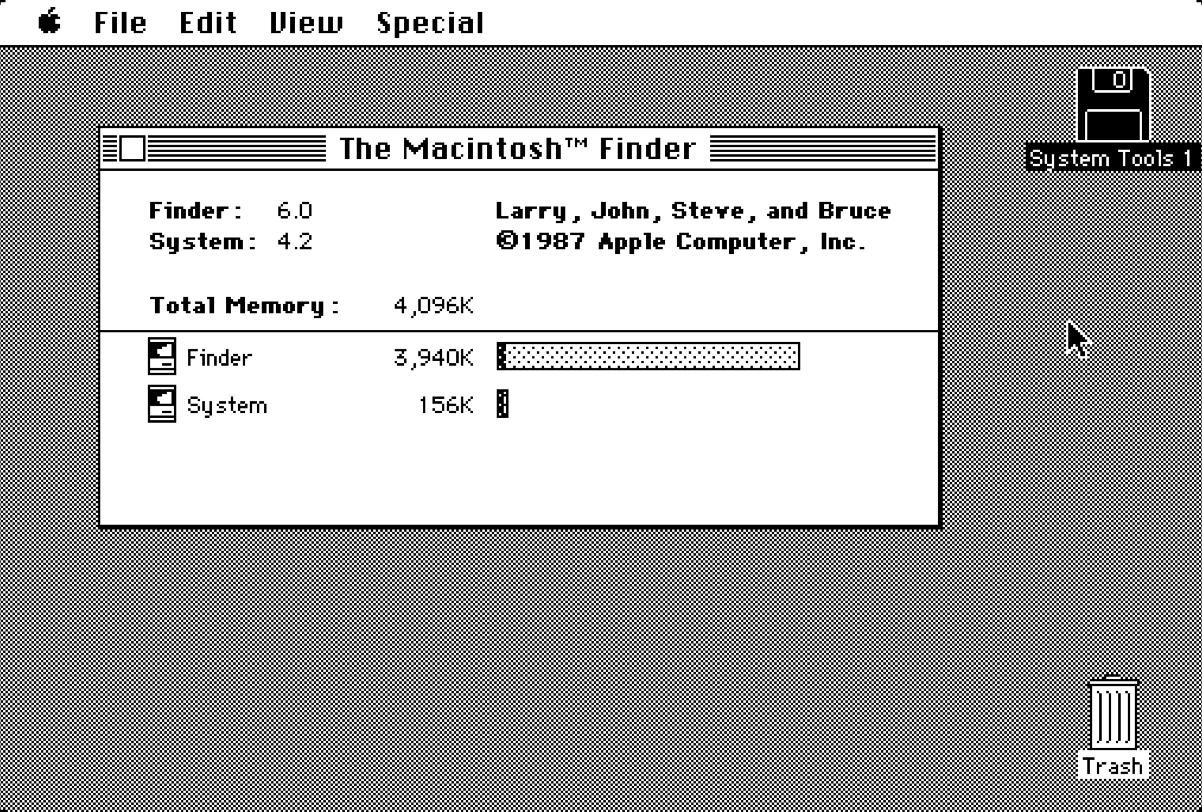
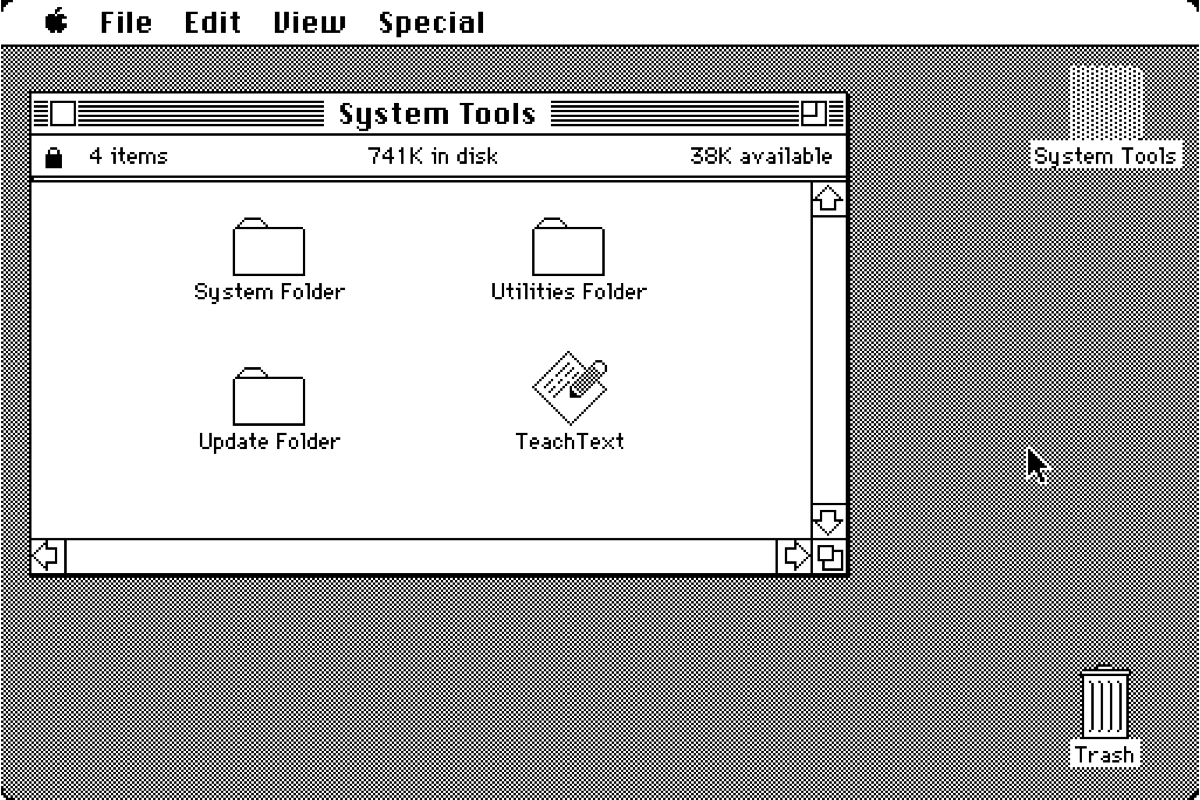
6.0
April 1988
68000 processor or later,
1 MB of RAM
7.0
May 1991
68000 processor or later,
2 MB RAM and 4 MB HD
7.1
October 1992
68000 processor or later,
2 MB of RAM and 4 MB HD
7.5
September 1994
68000, 68020, 68030, 68040 or PowerPC processor, 4 MB (68k) 8 MB (PPC) of RAM, and 21 MB HD
7.6
January 1997
32-bit clean 68030, 68040 or PowerPC processor, 8 MB of real RAM and 40 to 120 MB HD
8.0
July 1997
68040 or PowerPC processor, 12 MB of real RAM and 195 MB HD
8.1
January 1998
68040 or PowerPC processor, 12 MB of real RAM and 195 MB HD
8.5
October 1998
PowerPC processor, 16 MB of physical RAM and 150 to 250 MB HD
8.6
May 1999
PowerPC processor, 24 MB of RAM installed and 190 to 250 MB HD
9.0
October 1999
PowerPC processor, 32 MB of physical RAM and 190 to 250 MB HD
9.1
January 2001
PowerPC processor, 32 MB of physical RAM and 320 MB HD
9.2
June 2001
PowerPC G3 (original PowerBook G3 not supported), 32 MB of physical RAM and 320 MB HD
mac os classic
System 1
Das gesamte System wurde mit den ersten Macintosh 128k-Modellen auf einer 400 KB-Diskette ausgeliefert und enthielt auch eine separate Lerndiskette, die Ihnen die Verwendung der Maus beibrachte, genannt „Mousing Around“, was später zu „Mac Basics“ wurde. Obwohl es ein Durchbruch im Interface-Design war, brachte System 1.0 auch viele Kopfschmerzen und Inkonsistenzen mit sich. Am offensichtlichsten war das Kopieren von Disketten, das bis zu 20 Minuten und unzählige Diskettenwechsel dauern konnte (teilweise aufgrund des begrenzten Speichers des Mac). Beim Neuaufbau des Desktops wurden damals alle Ordner entfernt und alle Dateien auf der Stammebene der Festplatte abgelegt. Es konnte auch kein neuer Ordner erstellt werden. Stattdessen existierte immer ein Ordner mit dem Namen „leerer Ordner“ auf der Stammebene jeder Mac-formatierten Festplatte. Wenn Sie ihn umbenannten, erschien ein neuer „leerer Ordner“.
applemuseum.bott.org
System 2
Apple arbeitete fast ein Jahr lang an dem neuen System, bevor es der Öffentlichkeit zugänglich gemacht wurde. Der Großteil der Arbeit wurde am Finder geleistet, der von Version 1.1 auf 4.1 sprang, während das System nur bis 2.0 ging. Der Finder war jetzt viel schneller als je zuvor und vollgepackt mit neuen Funktionen. Benutzer konnten mit dem Befehl „Neuer Ordner“ einen neuen Ordner erstellen. Benutzer konnten jetzt zum ersten Mal die Ansicht des Ordners auf „Liste“ ändern, wodurch kleine Symbole neben den entsprechenden Dateinamen erstellt wurden. Benutzer konnten die Liste auch mit „Katalog drucken“ drucken, einem neuen Befehl im Dateimenü. Benutzer konnten jetzt auch das Betriebssystem mit dem Befehl im Spezialmenü herunterfahren. Datenträger konnten ausgeworfen werden, indem man sie in den Papierkorb zog. Minifinder wurde ebenfalls im Spezialmenü eingeführt. Es ermöglichte Benutzern, ihre bevorzugten Anwendungen auszuwählen, sodass beim Beenden einer Anwendung ein Dialogfeld mit Symbolen aller anderen Anwendungen angezeigt wurde, die sie ausgewählt hatten.